miRNA, as a organic marker, had extra and extra consideration lately as a result of necessary position it performs in most cancers. Currently, there are intensive research on miRNAs, amongst which miR-330-3p is reported to be implicated within the pathophysiological processes of numerous cancers.
However, little progress has been made within the mechanism of miR-330-3p in gastric most cancers.To discover the expression and related mechanism of miR-330-3p and PRRX1 in gastric most cancers (GC).
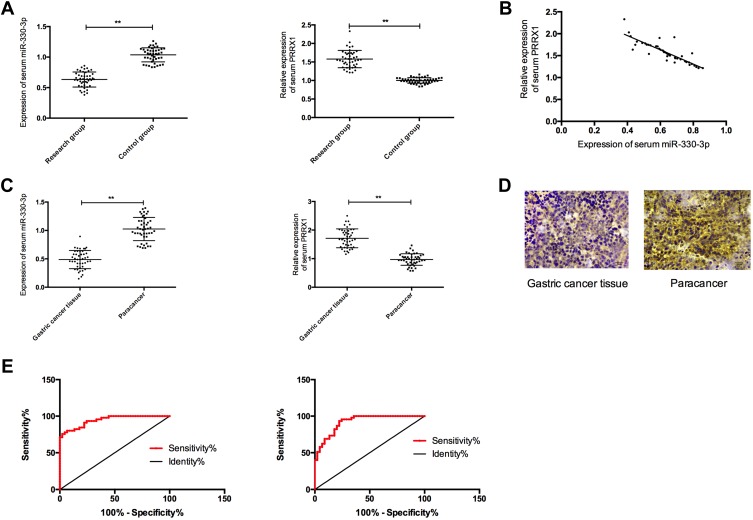
Forty-five GC sufferers (examine group), from whom paired GC and paracancerous tissues had been collected, and one other 45 wholesome topics (management group) who underwent bodily examination throughout the identical interval had been enrolled. In addition, GC cells and human gastric mucosa cells had been bought, and miR-330-3p-mimics, miR-330-3p-inhibitor, miR-NC, si-PRRX1, and sh-PRRX1 had been transfected into MKN45, SGC7901 cell. QRT-PCR was employed to evaluate the miR-330-3p and PRRX1 expressions within the samples, and the cell expressions of PRRX1, GSK-3β, p-GSK-3β, β-catenin, p-β-catenin, cyclin D1, N-cadherin, E-cadherin and vimentin had been evaluated by Western blot (WB). MTT,
Transwell and wound-healing experiments had been adopted to detect cell proliferation, invasion and migration.MiR-330-3p was under-expressed, whereas PRRX1 was extremely expressed within the serum of sufferers, each of which had an space beneath the curve (AUC) of greater than 0.9. MiR-330-3p and PRRX1 had been related to tumor diameter, TNM staging, lymph node metastasis and differentiation of GC sufferers.
Overexpression of miR-330-3p and inhibition of PRRX1 expression might suppress epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), proliferation, invasion and apoptosis of cells.
What is extra, WB assay confirmed that overexpressed miR-330-3p and inhibited PRRX1 might inhibit the expression ranges of p-GSK-3β, β-catenin, cyclin D1, N-cadherin and vimentin proteins, whereas elevating GSK-3β, p-β-catenin and E-cadherin protein expressions.
Dual-luciferase reporter assay confirmed that there was a focusing on relation between miR-330-3p and PRRX1. Furthermore, rescue experiments revealed that the cell proliferation, invasion, migration didn’t differ considerably between co-transfected miR-330-3p-mimics+sh-PRRX1, miR-330-3p-inhibitor+si-PRRX1 teams of MKN45 and SGC7901 and the miR-NC group (with out transfected sequences).
Overexpressed miR-330-3p can promote cell EMT, proliferation, invasion and apoptosis by inhibiting PRRX1-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which is predicted to be a possible therapeutic goal for GC.
KIF23 activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by direct interplay with Amer1 in gastric most cancers.
Increased expression of the kinesin member of the family 23 (KIF23) has been verified in gastric most cancers (GC) and its upregulation contributes to cell proliferation. Even although, the position of KIF23 has not been totally elucidated in GC, and the mechanisms of KIF23 as an oncogene stay unknown.
To additional establish its potential position in GC, we analyzed gene expression knowledge from GC sufferers in GEO and TCGA datasets. KIF23 was upregulated in GC, and elevated expression of KIF23 correlated with poor prognosis. Importantly, KIF23 inhibition not solely suppressed GC cell proliferation, tumorigenesis, but in addition migration and invasion, and arrested the cell cycle within the G2/M section.
Mechanistic investigations confirmed that KIF23 activated the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by straight interacting with APC membrane recruitment 1 (Amer1).
Furthermore, KIF23 exhibited aggressive binding with Amer1 to dam the affiliation of Amer1 with adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), thus relocating Amer1 from the membrane and cytoplasm to the nucleus and attenuating the power of Amer1 to negatively regulate Wnt/β-catenin signaling, leading to activation of this signaling pathway. Collectively, our findings demonstrated that KIF23 promoted GC cell proliferation by straight interacting with Amer1 and activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
